Chess Game Rules and Regulations 2022
An intellectual board game, chess is a great way to improve your mental abilities. The game is a two-on-two matchup between two people. If you want to learn tactics and strategy and beat strong opponents in chess, the rules of the game are not simple. Adults and children alike can, however, quickly learn the fundamentals of the game and get right into the action.
How To Set Up The Chess Board
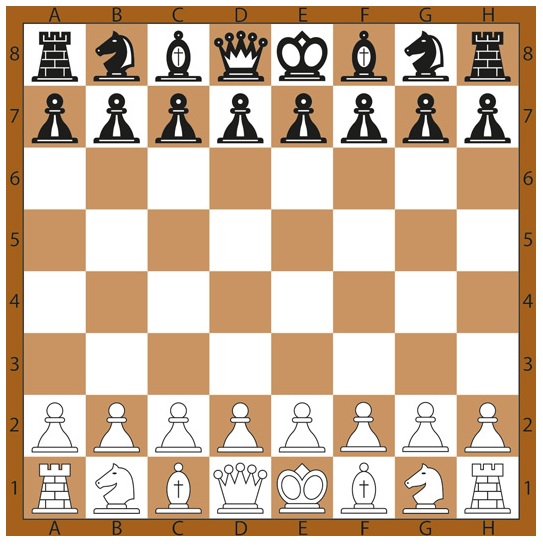
The game of chess follows a set of rules and regulations that dictate the placement and movement of pieces on the board. The chessboard consists of 64 squares, alternating between black and white. The proper arrangement of the board is determined by having a white square in the lower right corner.
Each player starts with 16 pieces, with specific patterns for their arrangement on the board. The first and eighth lines of the board have specific rules for placing the pieces:
- The rooks, which are castle-shaped pieces, occupy the corners of the board. The white rooks are placed on squares a1 and h1, while the black rooks go on squares a8 and h8.
- Next to the rooks are the knights, which resemble horses. The white knights are positioned on squares b1 and g1, while the black knights are placed on squares b8 and g8.
- Adjacent to the knights are the bishops, which have a tall hat-like appearance. The white bishops are placed on squares c1 and f1, while the black bishops go on squares c8 and f8. Each bishop should be placed on a square of the opposite color.
- The queen is positioned on a square of the same color as the piece. For example, the white queen is placed on a white square, and the black queen is placed on a black square.
- The king is placed next to the queen. The white king goes on square e1, and the black king is placed on square e8.
- Finally, all the pawns are positioned in a row in front of the other pieces. The white pawns occupy the second rank, from a2 to h2, while the black pawns are placed on the seventh rank, from a7 to h7.
In chess, each piece has a different value and importance. The queen is the most valuable piece, followed by the bishop and knight. The rook holds significant strategic importance, while the pawn is the least valuable piece.
Understanding the basic rules and regulations of chess is crucial for strategic gameplay. It emphasizes the importance of protecting and not unnecessarily jeopardizing your pieces. Sacrificing a less valuable piece can be a tactical decision to gain an advantage.
These rules are widely recognized and form the foundation of international chess rules. By adhering to these regulations, players can engage in a game of chess that is both strategic and fair.
Correct placement of pieces according to the classical scheme on the chessboard:
How The Game Of Chess Begins
In the game of chess, each player has 16 pieces in either black or white. The color of the pieces is typically determined by a random toss or other means. The player with the white pieces always makes the first move. The objective of chess is to checkmate the opponent’s king.
The game progresses by alternating turns between the players. Each move involves moving a piece from one square to another on the board, except in the case of castling where two pieces move simultaneously. When a piece is moved to a square occupied by an opponent’s piece, the opponent’s piece is captured and removed from the board. This type of move is referred to as a capture in chess terminology.
The ultimate goal is to checkmate the opponent’s king. Checkmate occurs when the opponent’s king is in a position where it is under attack and cannot make any legal moves to escape capture. This signifies the end of the game, with the player achieving checkmate emerging as the winner.
Understanding the basic rules and regulations of chess is vital for engaging in strategic gameplay. These rules outline how the pieces move, the objective of the game, and the concept of capturing opponent’s pieces. These regulations form the foundation of international chess rules and ensure a fair and enjoyable playing experience for all participants.
How Chess Pieces Move
1. King
In the game of chess, the king holds the greatest weight and significance. It has the ability to move in any direction—horizontally, vertically, or diagonally—to an unoccupied square on the board. However, the king cannot move to an adjacent square if it would put it in a position of being attacked by one of the opponent’s pieces.
The king possesses a special move known as castling, where it can move two squares towards a rook, and the rook simultaneously moves to the other side of the king. This move serves as a strategic maneuver to safeguard the king and improve its position on the board.
The primary objective of the king is to avoid capture by the opponent’s pieces. Protecting the king and ensuring its safety is crucial while strategically planning and coordinating with other pieces to achieve victory.
Understanding the rules and regulations of chess is essential to grasp the significance and role of each piece, including the king. These rules establish how the king moves, its limitations, and its strategic importance in the game. Adhering to these regulations, which form the basis of international chess rules, allows players to engage in fair and strategic gameplay.
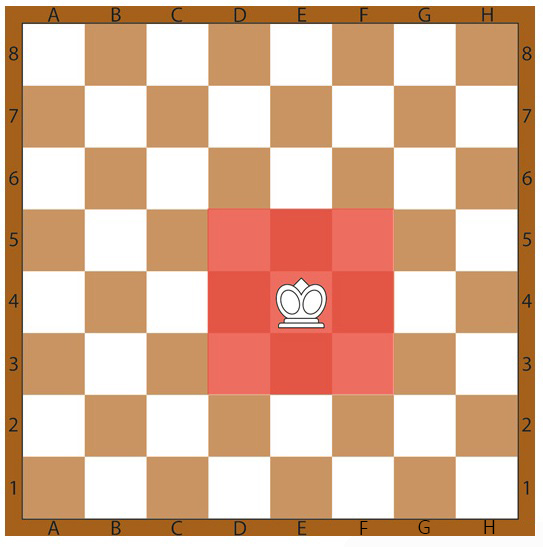
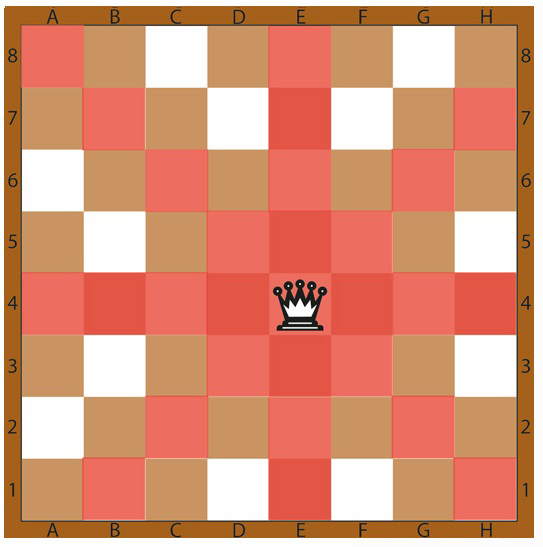
2. Queen
In the realm of chess, the queen stands as the second most influential piece on the board, just after the king. Traditionally, the value of a queen is equated to that of eight pawns. The queen possesses the remarkable ability to move any number of squares vertically, diagonally, or horizontally, as long as there are no obstructions along its path.
Renowned for its versatility and aggression, the queen often assumes a commanding role in controlling the center of the board, launching attacks on the opponent’s pieces, and providing support to other pieces in their strategic endeavors. Its unrestricted mobility renders it a formidable force in the game, serving as a crucial asset in the pursuit of victory.
A profound understanding of the rules and regulations of chess is vital to comprehend the significance and potential of each piece, including the queen. These rules establish the queen’s movement capabilities, its strategic importance, and its role in shaping the dynamics of the game. Adhering to these regulations, which form the foundation of international chess rules, ensures fair and engaging gameplay for all participants.
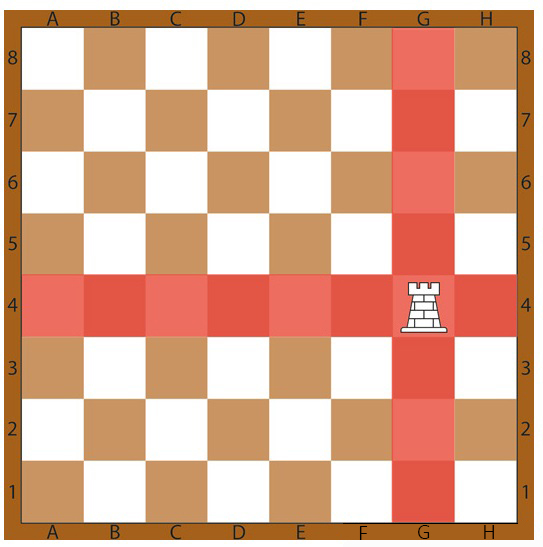
3. Rook
In the realm of chess, the rook stands as a powerful and formidable piece. It possesses the ability to move in a straight line, either horizontally or vertically, across the chessboard. The rook can traverse any number of squares along ranks and files, provided there are no obstructions in its path. This grants the rook the capability to move forward, backward, left, or right.
The movement of the rook is not impeded by the presence of other pieces on the board. However, the rook cannot leap over other pieces and can only occupy an empty square or capture an opponent’s piece by moving to its square.
Understanding the rules and regulations of chess is fundamental in comprehending the power and role of each piece, including the rook. These rules outline the rook’s movement capabilities, its strategic significance, and its contribution to the dynamics of the game. By adhering to these regulations, which form the bedrock of international chess rules, players can engage in fair and strategic gameplay.
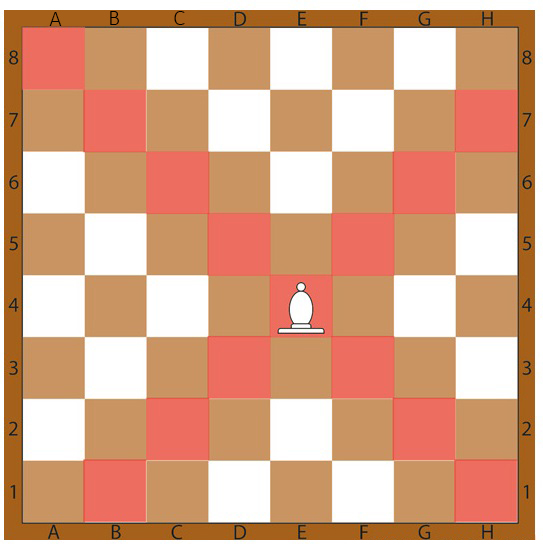
4. Bishop
In the game of chess, the bishop holds a unique and influential role. It moves diagonally across the board, with the ability to traverse any number of squares along the diagonals, provided there are no hindrances obstructing its path. At the start of the game, each player has two bishops—one positioned on light squares and the other on dark squares. Throughout the game, the bishop’s movement remains confined to the color of the square it initially occupies.
Endowed with the capacity to cover long distances and strike from a distance, the bishop emerges as a potent and strategic piece. Its diagonal movement allows it to assert control over important sectors of the board, enabling it to influence the course of the game and potentially engage in powerful attacks.
A comprehensive understanding of the rules and regulations of chess is pivotal in comprehending the strengths and role of each piece, including the bishop. These rules delineate the bishop’s movement patterns, its adherence to squares of a specific color, and its contribution to the overall dynamics of the game. By adhering to these regulations, which form the bedrock of international chess rules, players can engage in fair and strategic gameplay.
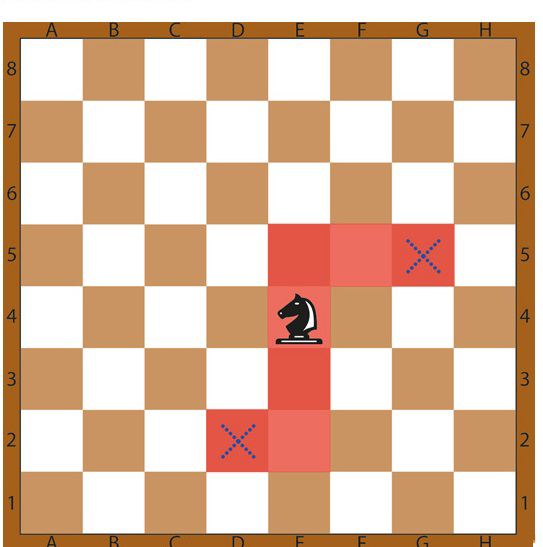
5. Knight
The letter “L” is the knight’s command to move. Basically, this means it moves two cells vertically and one horizontally at the same time (or two horizontally and one vertically). Despite the presence of other pieces, the knight is the only piece that can make a move through other pieces.
6. Pawn
In chess, the pawn is the lowest-valued piece, only capable of moving one square in any direction. This rule has two exceptions.
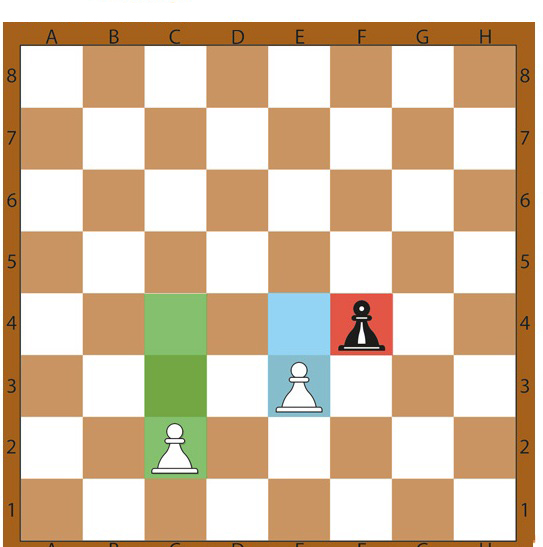
Exceptions:
- Capturing an opponent’s piece by a pawn. A pawn can capture any opponent’s piece if it is under capture – one square from it diagonally. In the case of a capture, the pawn moves to the square diagonally, and the captured opponent’s piece is eliminated from the game.
- Starting pawn move. On the first move, the pawn can move one or two squares straight.
Special Rules In Chess
Pawn Promotion
In the realm of chess, when a pawn reaches the opposite rank of the chessboard, a momentous event takes place—the pawn undergoes promotion. At this juncture, the pawn has the privilege of transforming into any piece of the same color: a rook, bishop, queen, or knight. Among these options, the most common and sought-after choice is the promotion to a queen, as it holds the highest value and power on the chessboard.
Pawn promotion holds immense significance, particularly in the endgame, as it can pave the way for the creation of powerful combinations or contribute to the attainment of a checkmate. The decision regarding which piece to promote the pawn to necessitates careful deliberation, as it can exert a profound influence on the ultimate outcome of the game.
Understanding the rules and regulations of chess is vital in comprehending the mechanics and impact of pawn promotion. These rules delineate the process by which pawns ascend to higher ranks and the choices available for their transformation. Adhering to these regulations, which form the foundation of international chess rules, ensures fair and strategic gameplay for all participants.
En Passant Rule Of Pawn
In the game of chess, a pawn has the ability to execute a special move called pawn capture en passant. This move can occur under specific circumstances when an opponent’s pawn makes its initial move by advancing two squares and lands beside a pawn of the opposing player. If this happens, the opposing player has the option to capture the advancing pawn as if it had only moved one square forward. The captured pawn is then removed from the board, and the capturing player’s piece occupies the square that was initially under attack by the defending player’s pawn.
The rules of chess do not prohibit this unique maneuver, allowing for strategic opportunities and tactical decisions. However, it is essential to note that this move is only available under the specific conditions mentioned above.
Understanding the rules and regulations of chess is crucial in comprehending the various moves and strategies available to players, including the pawn capture en passant. These rules establish the framework within which players can navigate the chessboard and engage in fair and strategic gameplay. Adhering to these regulations, which form the basis of international chess rules, ensures a level playing field and an enjoyable experience for all participants.
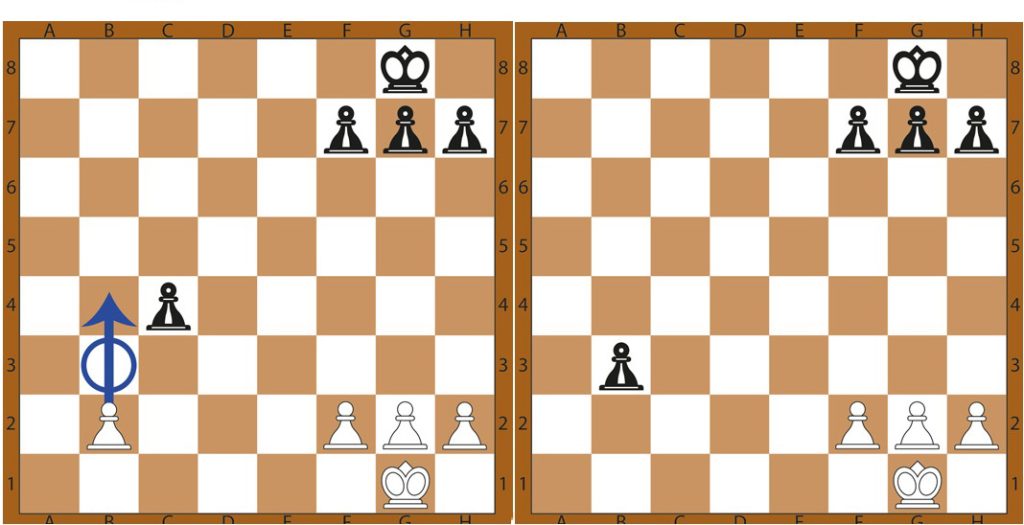
Castling In Chess
In the realm of chess, castling holds great significance as a pivotal move in the game. It serves a dual purpose: protecting the king and repositioning the rook to a more advantageous location on the board. During castling, the king is mobilized by moving two squares towards the rook. Subsequently, the rook maneuvers over the king, occupying the square on the opposite side.
Several conditions must be met for castling to be executed:
- The move must be the first for both the king and the rook involved.
- There must be no pieces between the king and the rook.
- The squares that the king moves through and lands on must be unoccupied.
- The squares that the king moves through and lands on must not be under attack by the opponent’s pieces.
- The king must not be in check.
Adhering to these rules ensures the validity of the castling move and allows players to reap its strategic benefits.
Understanding the rules and regulations of chess is crucial in comprehending the mechanics and limitations of castling. These rules establish the conditions under which this special move can be executed and contribute to fair and strategic gameplay. Adhering to these regulations, which form the foundation of international chess rules, ensures a level playing field and an enjoyable experience for all participants.
Checkmate In Chess
In the realm of chess, when the opponent’s piece poses a threat to the king, it is referred to as a check. Safeguarding the central piece of the game becomes paramount when the king is under check. The king can accomplish this by moving to a different square on the board where it is not under threat from the opponent’s pieces. Alternatively, the king can eliminate the threatening piece by capturing it if possible. Another strategy involves using one’s own piece to block or capture the attacking piece, although this often results in losing the blocking piece.
Checkmate is a term used to denote a situation where the king is under an inescapable check. In this scenario, the game comes to an end, and no further moves are required. Player 1 emerges victorious by repeatedly placing the opponent’s king in check.
Stalemate occurs when the king is not in check but is unable to make a legal move. In modern chess, this results in a draw being declared as the official outcome of the game. Stalemates can arise in certain situations where neither player can make a move that does not result in their own king being in check.
Understanding the rules and regulations of chess is essential in comprehending the dynamics of checks, checkmates, and stalemates. These rules establish the conditions for these outcomes and contribute to fair and strategic gameplay. Adhering to these regulations, which form the foundation of international chess rules, ensures a level playing field and an enjoyable experience for all participants.
Winning In Chess
- The player who has put check and checkmate on the opponent’s king is declared the winner.
- One of the participants gave up. In this case, the opponent is automatically declared the winner.
- The player has overdue the allotted time. His opponent is automatically declared the winner if he has enough pieces on the field to checkmate.
Draw In Chess
- By agreement between the players.
- The same moves and positions were repeated three times.
- Due to the position of the pieces on the board, the player cannot make his move.
- There are not enough pieces left on the board, which prevents the opponent from mating.
- 50 moves are made, but no capture was made during this period.
Tips For Beginner
As a beginner in the captivating world of chess, there are several key tips to help you enhance your game:
- Familiarize yourself with the fundamental rules and movements of each chess piece, as outlined in the basic rules and regulations of chess.
- Dedicate time to regular practice sessions, which will gradually develop your chess intuition and improve your decision-making abilities.
- Study and internalize fundamental principles, such as the importance of controlling the center of the board and developing your pieces harmoniously.
- Engage in solving tactical puzzles to sharpen your calculation skills and enhance pattern recognition, crucial aspects of successful gameplay.
- Analyze your completed games to identify mistakes, missed opportunities, and areas for improvement, as part of the learning process.
- Explore and study famous games played by grandmasters, allowing you to gain valuable insights into strategic planning and positional play.
- Play against opponents of varying skill levels to challenge yourself and learn from their strategies, gradually expanding your understanding of the game.
- Develop a solid opening repertoire and strive to understand the underlying ideas and principles behind each opening you choose to employ.
- Engage in longer time control games, granting you more time for deeper thinking, analysis, and strategic decision-making.
- Above all, remember to enjoy the process and have fun! Chess is an endless journey of learning and discovery.
By adhering to these tips and immersing yourself in the beauty of chess, you will steadily progress and find greater enjoyment in this timeless game of strategy and intellect.
